No products found.
No products found.
04 August 2025
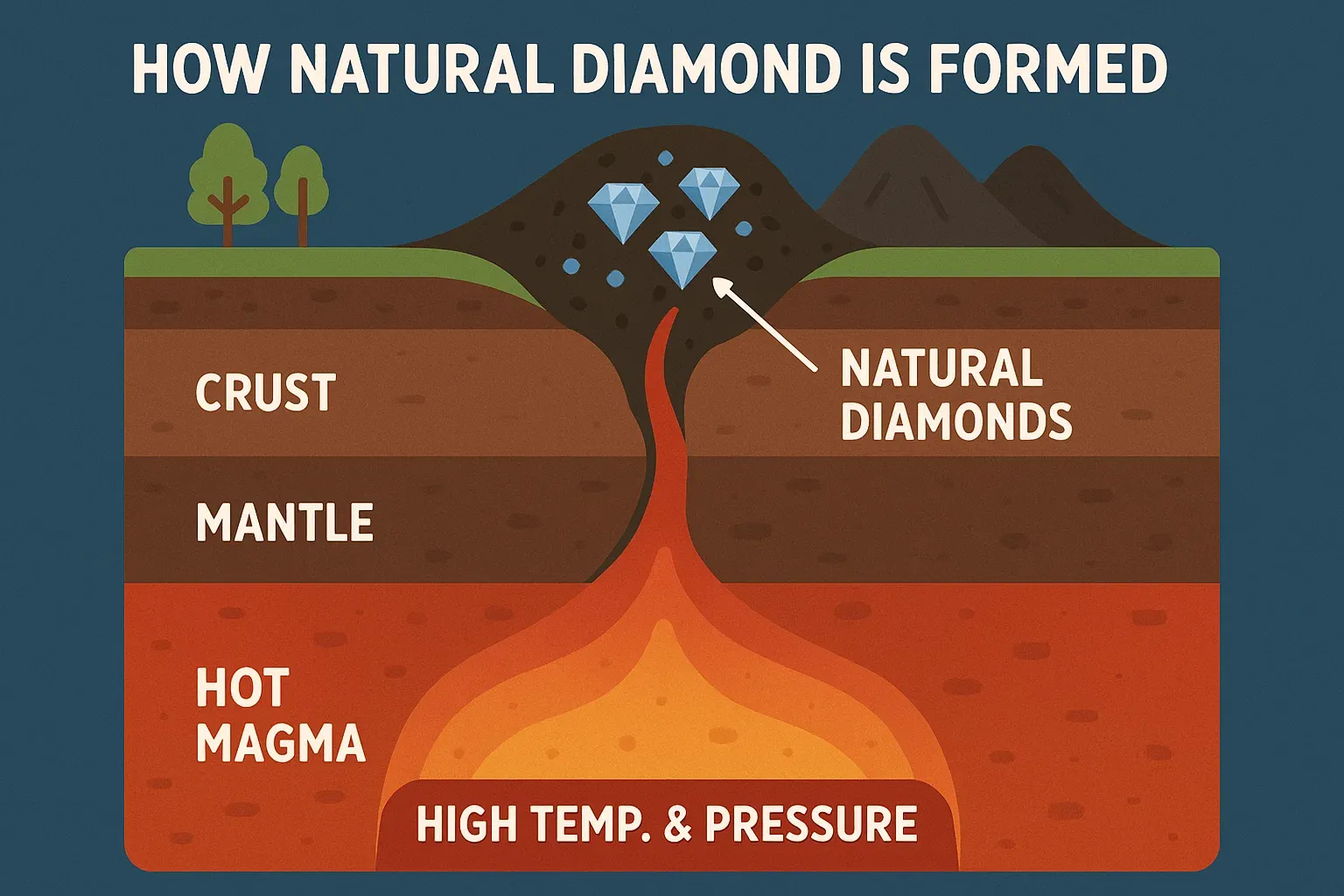
Diamonds have fascinated humanity for centuries. Known as the hardest natural substance on Earth, they are symbols of love, strength, and eternity. But have you ever wondered how natural diamond is formed? The process is as mysterious as the gems themselves, taking billions of years beneath the Earth’s surface.
At the same time, the jewellery industry is evolving. Today, brands like AYAANI are revolutionising the world with lab-grown diamond jewellery, offering the same brilliance as natural diamonds but with a sustainable and ethical twist.
Natural diamonds aren’t made overnight. They require a perfect balance of heat, pressure, and time deep within the Earth’s mantle. This extraordinary process makes each diamond truly one of a kind, often referred to as “a miracle of nature.”
Both are chemically, physically, and optically identical. The only difference lies in their origin.
Diamonds are pure carbon crystals arranged in a unique lattice structure. This arrangement gives diamonds their unparalleled hardness and sparkle.
Carbon atoms deep in the Earth’s mantle bond together in extraordinary conditions, forming these precious gems.
Diamonds form 150–200 kilometres below the Earth’s surface, where temperatures reach over 1,000°C and pressures soar above 725,000 pounds per square inch.
Diamonds travel to the surface via volcanic pipes known as kimberlite eruptions, which transport them at incredible speeds.
Diamonds were first discovered in India nearly 2,500 years ago and were once considered symbols of divine power. Famous natural diamonds like the Koh-i-Noor and the Hope Diamond continue to mesmerise collectors worldwide.
While stunning, natural diamond mining comes at a cost.
There are two main methods:
Lab-grown diamonds are real diamonds, identical in structure, brilliance, and durability. Even gemologists need advanced equipment to tell them apart.
Lab-grown diamonds use less land, water, and energy, making them an eco-friendly alternative.
AYAANI is a modern jewellery brand dedicated to ethical luxury. They specialise in lab-grown diamonds that are as timeless and radiant as their natural counterparts.
AYAANI offers a wide range of rings, earrings, necklaces, and bracelets, each piece crafted with care, precision, and elegance. The jewellery isn’t just beautiful; it’s a conscious choice for the future.
Natural diamonds are extraordinary marvels formed over billions of years. But as the world evolves, lab-grown diamonds are becoming the future of jewellery, ethical, sustainable, and just as beautiful.
With AYAANI’s lab-grown diamond jewellery, you can celebrate luxury without compromising the planet. Whether it’s an engagement ring, a gift, or a personal statement, AYAANI makes sure every piece tells a story of brilliance and responsibility.
Make the switch today, because true beauty shines brighter when it’s conscious.
1. How are diamonds formed from coal?
They usually aren’t. Most natural diamonds form deep in the Earth, not from coal, but from pure carbon under high pressure and temperature.
2. How are black diamonds formed?
Black diamonds (carbonado) are made of many tiny crystals with graphite and other minerals inside, giving them a dark colour.
3. How are blue diamonds formed?
Blue diamonds get their colour from boron atoms trapped in the diamond’s structure during formation.
4. How are colored diamonds formed?
Colored diamonds form when trace elements or structural changes occur during formation, affecting how they absorb light.
5. How are diamonds formed for dummies?
Deep underground, carbon gets squeezed under extreme pressure and heat. Over time, it turns into diamonds.
6. How are green diamonds formed?
Green diamonds get their colour from natural radiation that alters the surface of the stone as it forms.
7. How are pink diamonds formed?
Pink diamonds likely get their colour from pressure twisting the crystal structure, changing how light passes through.
8. How are red diamonds formed?
Red diamonds form like pink ones; intense pressure changes the crystal structure, but the colour is even more vivid.
9. How are yellow diamonds formed?
Yellow diamonds get their colour from nitrogen atoms mixed into the carbon structure during formation.
10. How is it formed from carbon?
Carbon atoms bond tightly in a crystal pattern under intense heat and pressure, turning into diamond over millions of years.
11. What is the timeline for a natural diamond to form?
Natural diamonds can take 1 to 3 billion years to form deep within the Earth.
12. Are lab-grown diamonds real diamonds?
Yes! Lab-grown diamonds are chemically and physically identical to natural diamonds.
13. Can you tell the difference between natural and lab-grown diamonds?
To the naked eye, no. Only specialised equipment can distinguish them.
14. Which is better for the environment: natural or lab-grown diamonds?
Lab-grown diamonds are far more sustainable, with minimal ecological impact.
15. Do lab-grown diamonds hold value like natural diamonds?
While natural diamonds may have higher resale value, lab-grown diamonds are more affordable and ethical.
16. Why should you choose AYAANI’s lab-grown diamond jewellery?
AYAANI offers sustainability, affordability, and unmatched craftsmanship, making it the perfect choice for modern buyers.
17. What type of rock turns into a diamond?
Carbon-rich rocks in Earth’s mantle can turn into diamonds, especially in volcanic rocks called kimberlite.
18. Why is diamond so expensive?
Because it's rare, takes millions of years to form, and is in high demand for jewellery and tools.
19. What is the difference between a diamond and a crystal?
A diamond is a type of crystal made only of carbon. "Crystal" is a general term for any solid with an ordered atomic structure.
20 How many diamonds are there in the world?
Trillions exist, but only a small percentage are gem-quality and used in jewellery.
21. Which stone is equal to a diamond?
Lab-grown diamond looks identical and have the same hardness and structure as a natural diamond. That’s because it is a diamond, just created in a lab rather than mined from the earth.
22. What is the process of making a diamond called?
It's called crystallisation in nature, or High Pressure High Temperature (HPHT) or Chemical Vapour Deposition (CVD) in labs.
© 2025, AYAANI DIAMONDS. Developed & Maintained By Nothing Info, Designed & Marketing By Kyros Solution.